Hansen’s disease, also known as leprosy, is one of the oldest known infectious diseases. It affects the skin, nerves, upper respiratory tract, and eyes. Though it has been stigmatized for centuries, modern science has made significant strides in both the understanding and treatment of this disease. With the development of multi-drug therapy (MDT), the cure for Hansen’s disease has become more accessible than ever. In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and most importantly, the cure for Hansen’s disease, providing a comprehensive overview to raise awareness and promote understanding.
What is Hansen’s Disease?
Hansen’s disease is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium leprae, which primarily affects the skin, peripheral nerves, mucosal surfaces of the upper respiratory tract, and the eyes. It is a chronic infectious disease that has a long incubation period, sometimes taking several years to develop symptoms after exposure to the bacteria.
Hansen’s disease can be categorized into two forms: paucibacillary (PB) and multibacillary (MB), depending on the number of bacteria present in the body. PB involves a few lesions and fewer bacteria, while MB involves multiple lesions and a higher bacterial load.
While Hansen’s disease is contagious, it is not highly infectious. The bacteria are typically spread through respiratory droplets, and prolonged contact with an untreated individual is needed for transmission. Today, due to modern antibiotics and effective treatment, Hansen’s disease is no longer a significant public health threat.
Symptoms of Hansen’s Disease
The symptoms of Hansen’s disease can vary depending on the form of the disease. Common symptoms include:
- Skin lesions: These are often lighter or darker than the surrounding skin and may become numb or lose sensation.
- Numbness: People with Hansen’s disease may experience loss of feeling in their hands, feet, and face, which can lead to injury or burns that go unnoticed.
- Muscle weakness: The disease can affect the nerves, leading to muscle weakness or paralysis, especially in the hands and feet.
- Eye problems: Untreated Hansen’s disease can cause eye damage, leading to blindness if not addressed.
- Nasal issues: In some cases, the infection can damage the nasal passages, leading to nosebleeds or a collapsed nose.
If left untreated, Hansen’s disease can cause severe disfigurement, nerve damage, and other complications. However, with the right treatment, these issues can be prevented.
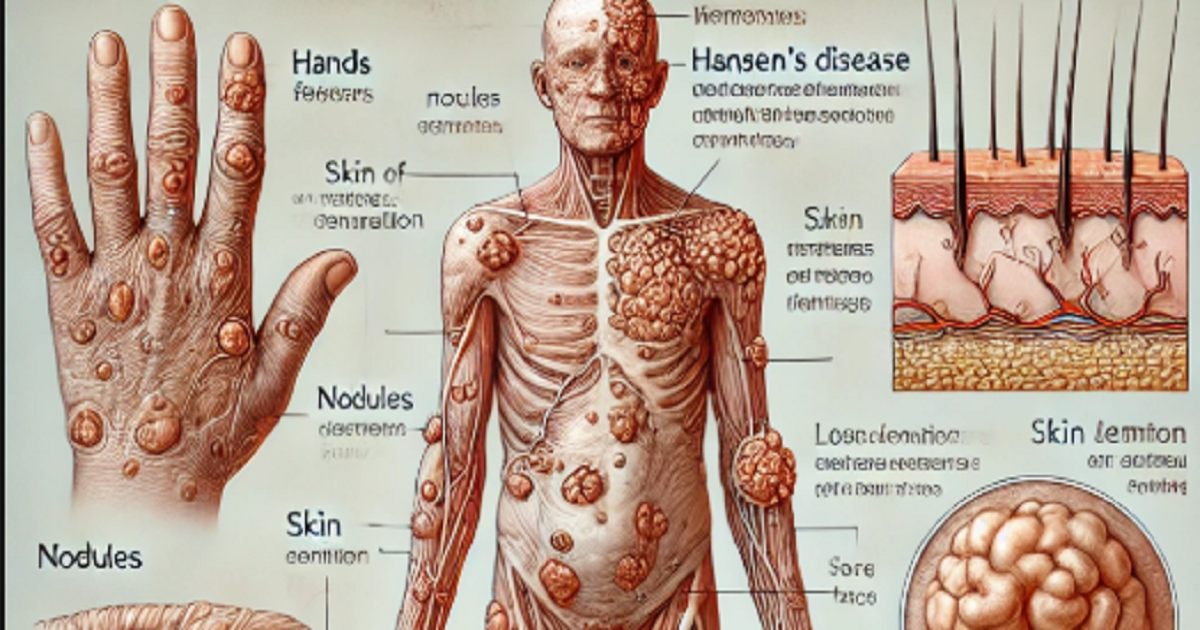
Diagnosis of Hansen’s Disease
Diagnosing Hansen’s disease typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. The doctor will examine the patient for characteristic skin lesions, loss of sensation, and other physical signs. A biopsy of the affected tissue may be conducted to confirm the presence of Mycobacterium leprae.
In some cases, additional tests, such as blood tests or skin smears, may be required. Once diagnosed, the disease is classified as either paucibacillary (PB) or multibacillary (MB), which will guide the treatment plan.
Cure for Hansen’s Disease: The Role of Multi-Drug Therapy (MDT)
For decades, Hansen’s disease was a feared condition with no effective treatment. However, with the advent of multi-drug therapy (MDT) in the 1980s, a cure for Hansen’s disease became widely accessible. MDT is a combination of antibiotics that work together to kill Mycobacterium leprae and prevent the development of drug resistance.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has provided MDT free of charge to patients worldwide. MDT typically involves a combination of three antibiotics:
- Dapsone: This antibiotic is used to inhibit the growth of the bacteria and is a key component in treating Hansen’s disease.
- Rifampicin: Rifampicin helps to kill the bacteria and prevent them from multiplying.
- Clofazimine: This drug has both antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties and is used to treat more severe cases of Hansen’s disease.
The duration of MDT treatment can vary depending on the form of the disease. For paucibacillary cases, treatment generally lasts for six months, while multibacillary cases may require up to 12 months of therapy. In some cases, prolonged treatment may be necessary to ensure the infection is completely eradicated.
How Effective is MDT in Curing Hansen’s Disease?
MDT has proven to be highly effective in curing Hansen’s disease, especially when started early in the disease’s progression. The combination of antibiotics effectively kills Mycobacterium leprae, preventing the spread of the bacteria and reducing the risk of complications, including nerve damage and disability.
After completing the full course of MDT, most patients are cured and are no longer contagious. However, it is important to note that even after treatment, some patients may continue to experience nerve damage or other residual effects. This highlights the importance of early diagnosis and treatment to prevent long-term complications.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
The key to successfully curing Hansen’s disease lies in early diagnosis and timely treatment. If diagnosed early, the disease can be effectively managed with MDT, preventing disability and reducing the risk of transmission. However, if left untreated, Hansen’s disease can lead to severe nerve damage, deformities, and other debilitating complications.
Since Hansen’s disease has a long incubation period, individuals may not exhibit symptoms for years after being exposed to the bacteria. This makes it essential for healthcare providers to be vigilant and consider the possibility of Hansen’s disease in patients presenting with suspicious symptoms such as skin lesions and numbness.
Stigma and Public Awareness
Although Hansen’s disease is now treatable, it continues to be associated with stigma and fear in many parts of the world. Historically, individuals with Hansen’s disease were ostracized and isolated due to misconceptions about the disease. This stigma can delay diagnosis and treatment, as individuals may fear seeking medical help.
In many countries, efforts are being made to raise awareness about Hansen’s disease and to educate the public that it is no longer a disease that leads to disfigurement and death. The development of MDT has transformed Hansen’s disease from a feared condition to a manageable illness, and with the right care, most people living with the disease can live healthy, productive lives.
Prevention of Hansen’s Disease
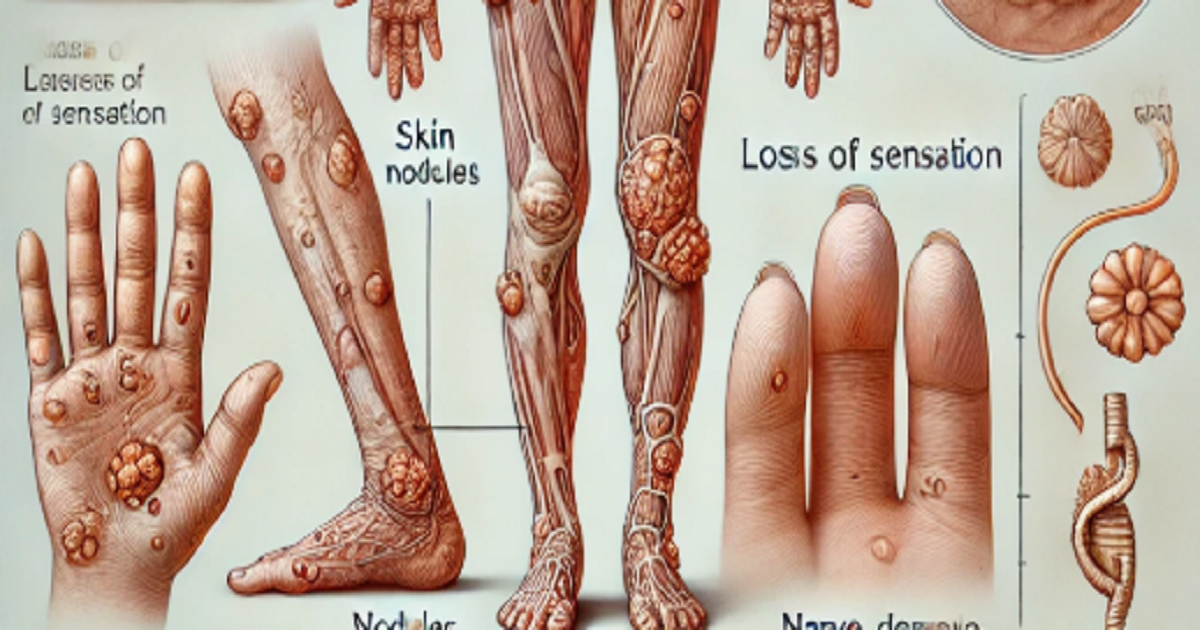
While there is no vaccine currently available to prevent Hansen’s disease, there are a few measures that can reduce the risk of transmission. These include:
- Early diagnosis and treatment: As discussed earlier, prompt treatment with MDT can prevent the spread of the disease.
- Avoiding prolonged contact: Hansen’s disease is primarily spread through respiratory droplets, so avoiding prolonged close contact with untreated individuals can help reduce the risk of transmission.
- Improved hygiene: Good hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing, can help reduce the risk of infection.
The Future of Hansen’s Disease Treatment and Cure
Though MDT remains the gold standard in the treatment of Hansen’s disease, research is ongoing to further improve treatment outcomes and explore additional therapies. Scientists are investigating new drugs that may shorten the duration of treatment or help manage the residual nerve damage that some patients experience after treatment.
Furthermore, public health campaigns continue to focus on raising awareness and reducing the stigma associated with Hansen’s disease, which is essential for ensuring that individuals seek treatment early.
In conclusion, the cure for Hansen’s disease is well-established thanks to the advent of multi-drug therapy (MDT), a combination of antibiotics that has proven highly effective in eliminating the bacteria responsible for the disease. With early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, individuals with Hansen’s disease can be cured and lead healthy lives.
While the stigma surrounding Hansen’s disease still exists in some parts of the world, awareness campaigns and global health initiatives are helping to reduce fear and promote understanding. The key to overcoming Hansen’s disease lies in education, early detection, and access to treatment. With continued progress in both medical research and public health efforts, Hansen’s disease can be eradicated, and those affected can live free from its debilitating effects.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of Hansen’s disease, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Early treatment with MDT can prevent complications and lead to a full recovery. With the right care, Hansen’s disease is no longer a cause for fear, and its cure is within reach for everyone.
FAQ: Cure for Hansen’s Disease (Leprosy)
Hansen’s disease, commonly known as leprosy, is an ancient disease that has caused fear and stigma for centuries. However, with the advent of modern medical treatment, the disease is now treatable and manageable. Below are some frequently asked questions (FAQ) about Hansen’s disease, providing insights into its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and cure.
What is Hansen’s Disease (Leprosy)?
Hansen’s disease, or leprosy, is a chronic infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium leprae. It primarily affects the skin, nerves, mucous membranes, and eyes. While it is treatable today, it has historically been surrounded by fear and stigma due to its disfiguring symptoms and long incubation period.
What Causes Hansen’s Disease?
Hansen’s disease is caused by Mycobacterium leprae, a bacterium that thrives in cooler areas of the body, such as the skin and nerves. The exact method of transmission is not fully understood, but it is believed that the disease spreads through prolonged close contact with an untreated individual via respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing.
How Does Hansen’s Disease Spread?
Although Hansen’s disease is contagious, it is not highly infectious. It spreads primarily through respiratory droplets when an untreated person coughs or sneezes. Prolonged close contact is necessary for transmission, making casual contact with infected individuals low-risk. Most people who are exposed to the bacteria do not develop the disease, likely due to immunity in the general population.
What Are the Symptoms of Hansen’s Disease?
The symptoms of Hansen’s disease can vary depending on the form of the disease (paucibacillary or multibacillary). Some common symptoms include:
- Skin Lesions: Light or dark patches on the skin that may lose sensation or become numb.
- Numbness: Loss of feeling in the affected areas, especially the hands, feet, and face.
- Muscle Weakness: Nerve damage can lead to muscle weakness, particularly in the extremities.
- Eye Problems: If left untreated, the disease can affect the eyes, potentially leading to blindness.
- Nasal Issues: Damage to the nasal passages can result in nosebleeds or a collapsed nose.
Symptoms can take several years to develop after exposure, making early diagnosis important for effective treatment.
How Is Hansen’s Disease Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Hansen’s disease involves both clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. Healthcare providers will look for characteristic skin lesions, numbness, and muscle weakness. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to check for the presence of Mycobacterium leprae. Additional tests like blood smears may also be conducted to confirm the diagnosis.
There are two main types of Hansen’s disease:
- Paucibacillary (PB): Fewer lesions and bacteria present.
- Multibacillary (MB): Multiple lesions and a higher bacterial load.
The classification of the disease helps guide treatment decisions.
Is There a Cure for Hansen’s Disease?
Yes, Hansen’s disease is curable today, thanks to the development of multi-drug therapy (MDT). MDT consists of a combination of antibiotics that effectively kill Mycobacterium leprae and prevent the development of drug resistance. With early and consistent treatment, most individuals can be cured of the disease.
What is Multi-Drug Therapy (MDT)?
Multi-drug therapy (MDT) is the standard treatment for Hansen’s disease. It is a combination of three antibiotics:
- Dapsone: Inhibits bacterial growth and is the main drug used in treatment.
- Rifampicin: Kills the bacteria and helps prevent them from multiplying.
- Clofazimine: Has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, and is particularly useful for more severe cases.
MDT treatment typically lasts from 6 months for paucibacillary cases to 12 months for multibacillary cases. In some cases, treatment may be extended.
How Effective is MDT in Treating Hansen’s Disease?
MDT is highly effective in curing Hansen’s disease, especially when started early. It kills the bacteria, prevents transmission, and reduces the risk of long-term complications, such as nerve damage. After completing the full course of MDT, most patients are no longer contagious. However, some individuals may experience residual nerve damage even after the infection is eradicated, making early treatment crucial.
Can Hansen’s Disease Be Prevented?
Currently, there is no vaccine to prevent Hansen’s disease. However, early diagnosis and prompt treatment can prevent complications and stop the spread of the disease. Additionally, good hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing, can help reduce the risk of infection. Avoiding prolonged contact with untreated individuals is another measure that can minimize the risk.
How Long Does It Take to Be Cured of Hansen’s Disease?
The length of treatment depends on the form of Hansen’s disease:
- Paucibacillary (PB): Treatment lasts for approximately 6 months.
- Multibacillary (MB): Treatment can last up to 12 months.
After completing the full course of MDT, patients are usually cured. However, long-term nerve damage may remain, so regular check-ups are essential.
Can People with Hansen’s Disease Live Normal Lives?
Yes, most individuals with Hansen’s disease can lead normal, healthy lives after completing treatment. MDT effectively cures the disease, and with early diagnosis, the risk of disability and disfigurement is minimized. However, those who have experienced nerve damage may need ongoing care and rehabilitation to manage residual symptoms, such as muscle weakness or numbness.
What Happens If Hansen’s Disease Is Left Untreated?
If left untreated, Hansen’s disease can cause severe nerve damage, deformities, and other complications. Chronic nerve damage can lead to muscle weakness, loss of sensation, and disability. In some cases, untreated Hansen’s disease can also cause blindness or irreversible damage to the nose and other facial features. However, with the availability of MDT, untreated cases are rare today.
What Is the Stigma Around Hansen’s Disease?
Historically, Hansen’s disease was surrounded by significant stigma and fear. This was largely due to misconceptions about its contagiousness, as well as its disfiguring symptoms in untreated individuals. The stigma led to discrimination and social isolation for people with the disease.
Today, with effective treatment available and public awareness campaigns, efforts are being made to reduce the stigma and educate the public that Hansen’s disease is curable and no longer a threat when treated properly. Awareness and education are key to ensuring that people seek timely medical attention.
How Can I Support Someone with Hansen’s Disease?
Supporting someone with Hansen’s disease involves offering emotional support and encouraging them to seek early treatment. Educating yourself and others about the disease helps to reduce the stigma surrounding it. Show compassion, as individuals with Hansen’s disease often face social isolation due to misconceptions about the disease.
Is There Ongoing Research Into Hansen’s Disease?
Yes, research into Hansen’s disease is ongoing, with a focus on improving treatment options, shortening the duration of therapy, and managing long-term complications such as nerve damage. Studies are also exploring the development of vaccines and better diagnostic methods. With continued research, it is possible that even more effective treatments and preventive measures will emerge.
Where Can I Get Treatment for Hansen’s Disease?
Treatment for Hansen’s disease is widely available and can be obtained through healthcare providers around the world. The World Health Organization (WHO) provides MDT free of charge to patients, ensuring that everyone has access to the necessary medications. If you suspect you have Hansen’s disease, it is important to consult a doctor who can provide a diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
How Can I Help Raise Awareness About Hansen’s Disease?
To help raise awareness about Hansen’s disease, you can:
- Educate others: Share accurate information about the disease, its treatment, and its cure.
- Support organizations: Contribute to or volunteer with organizations working to reduce the stigma associated with Hansen’s disease.
- Advocate for early diagnosis: Encourage individuals who may be at risk to seek medical attention promptly.
By educating others and reducing stigma, we can help eradicate Hansen’s disease and support those living with it.
In conclusion, Hansen’s disease is no longer the feared condition it once was. With the availability of multi-drug therapy (MDT), it is entirely treatable and curable. Early diagnosis, timely treatment, and public education are crucial in managing the disease, ensuring that those affected can live full and healthy lives.












5 thoughts on “Cure for Hansen’s Disease (Leprosy) :Types, Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment”